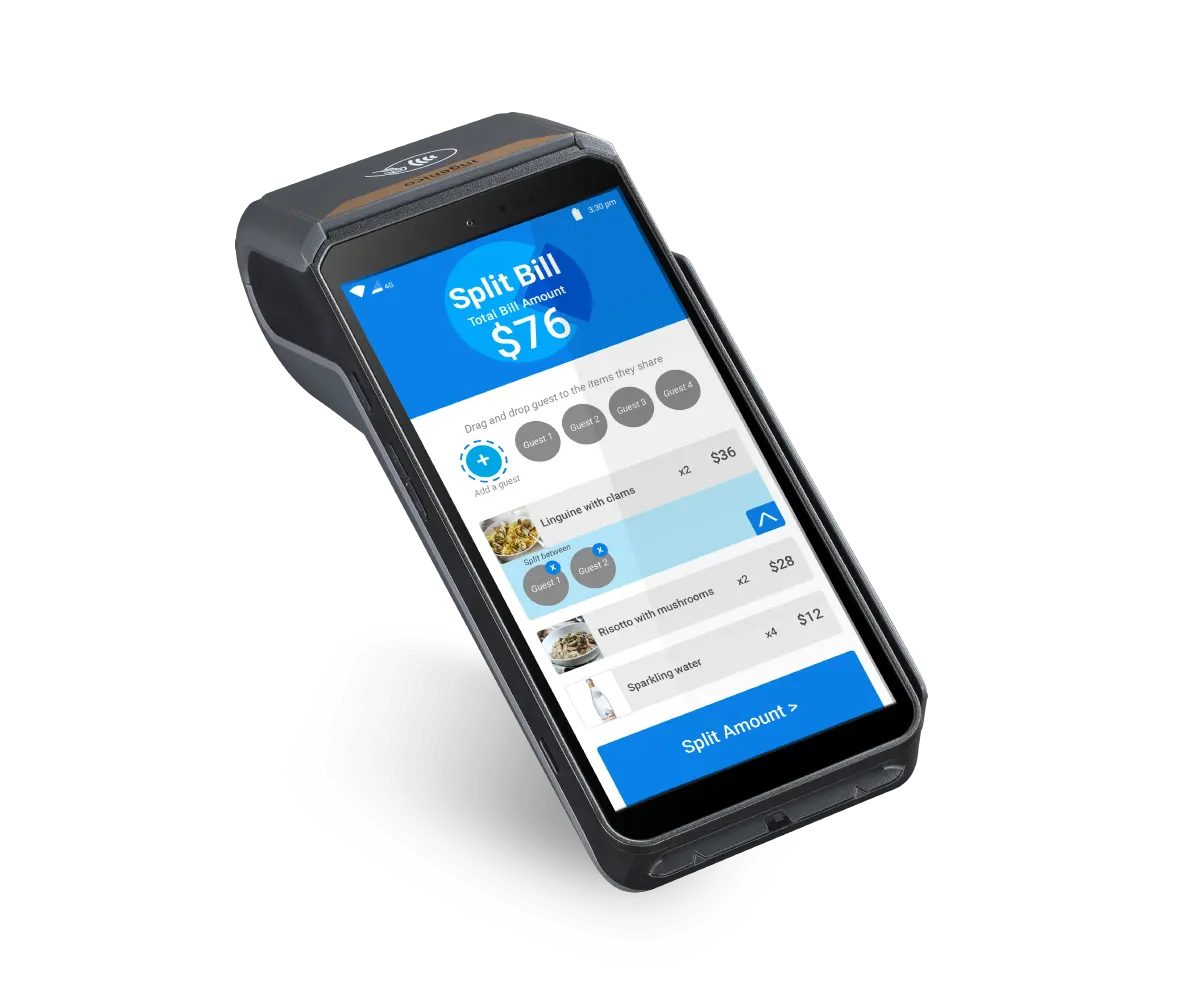
Payment terminal and card reader cost comparison
| Card payment provider – Standalone – UK | Card reader cost | Payment terminal cost | Payment Fees cost |
| Sumup | £39.00 | £139.00 | 1.69% per transaction |
| Zettle | £29.00 | £149.00 | 1.75% per transaction |
| Square | £19.00 | £149.00 | 1.75% per transaction |
| Gobal Payments | rental | rental | 1.50% per transaction |
| Takepayments | rental | rental | 1.00% per transaction |
| Dojo | £0.00 | £0.00 | 1.4% + £0.05 per transaction |
| Clover | £49.00 | £599.00 | 1.8% per transaction |
| Barclaycard | rental | rental | 1.6% per transaction |
| MyPOS | 39 | 179 | 1.10% + £0.07 per transaction |
| Revolut reader | na | na | 0.8% + £0.02 per transaction |
How do Card Machines work in the UK?
Card machines in the UK, also known as point-of-sale (POS) terminals or card payment terminals, are devices used to process debit and credit card transactions. These machines play a crucial role in facilitating electronic payments for goods and services. Here’s how card machines typically work in the UK:
- Card Insertion or Swipe: The customer inserts their chip-enabled debit or credit card into the card reader slot or swipes the magnetic stripe (if available). Many newer card machines in the UK support contactless payments, where the customer can simply tap their card or mobile device on the terminal to make a payment.
- Connection: The card machine connects to the payment network using various methods, including wired Ethernet connections, Wi-Fi, or cellular data (GPRS/3G/4G). This connection is essential for processing the transaction and communicating with the payment processor.
- Data Encryption: Once the card is inserted or tapped, the card machine encrypts the cardholder’s data and sends it securely to the payment processor. Encryption ensures that sensitive information like card numbers and personal identification numbers (PINs) are protected from unauthorized access.
- Transaction Verification: The payment processor sends the transaction details to the cardholder’s bank (issuing bank) for verification. The issuing bank confirms whether the customer has sufficient funds in their account to cover the transaction or whether the card is valid for the purchase.
- Authorization: If the cardholder’s bank approves the transaction, an authorization code is generated and sent back to the card machine through the payment network. This code indicates that the payment has been approved.
- Customer Interaction: Depending on the type of card machine, the customer may be prompted to enter their PIN for added security. For contactless payments, the transaction may not require a PIN for small amounts.
- Receipt Options: After the transaction is authorized, the card machine typically offers options for generating a receipt. This could be a printed receipt, an emailed receipt, or no receipt at all, based on the customer’s preference.
- Transaction Completion: Once the receipt is generated or the customer’s preference is recorded, the card machine finalizes the transaction. It may display a confirmation message on the screen, indicating that the payment has been successfully processed.
- Settlement: At the end of the day or a specified time period, the merchant initiates a settlement process. This involves transmitting all the authorized transactions to the payment processor, which then transfers the funds from the customer’s accounts to the merchant’s account.
- Funds Transfer: The settled funds are transferred from the cardholder’s bank to the merchant’s bank account. This typically takes a couple of business days to complete.
It’s important to note that card machines in the UK need to adhere to various regulations and security standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), to ensure the protection of customer data and payment information.